Chilly Fall Morning

Photo by Richard Luckin
Click to enlarge
What's happening in Golden today?
Events for Monday, Oct. 14th
- All day - CURRENT EXHIBITS AT THE MUSEUMS
- All day - Live Workouts with Community Center Pros
- All day - Golden History Tours
- 10:15-10:45AM - Let's Dance - Registration Required
- 1-2:30PM - Cybersecurity Awareness
- 2-3PM - Virtual: Active Minds Monday
- 5:30-7:30PM - The Fundamental Principles of Art
- 6-9PM - Teach Me to Play! Mondays
- 6PM - Halloween Trivia Night
For more information, click the item above or visit the Golden Today Calendar
Holidays

Golden Post Office - Google Street Images
There are a variety of holidays at this time of the year.
The State of Colorado observes Frances Xavier Cabrini Day on the first Monday in October, so state offices were closed last Monday.
The Federal government observes Columbus Day on the second Monday in October (that's today), so Federal offices are closed and there will be no mail delivery.
This is also Indigenous Peoples Day. The City of Golden observes this holiday, so the City offices are closed today.
Jefferson County doesn't observe any of the holidays, so school is in session and the County offices and the library are open today.
1-2:30PM Cybersecurity Awareness

Stay safe on the Internet and protect yourself from cybercriminals.
Prerequisites: Basic Computer skills, including using a mouse and keyboard.
Golden Library
1019 10th Street (map)
Golden Wildlife: Bobcats

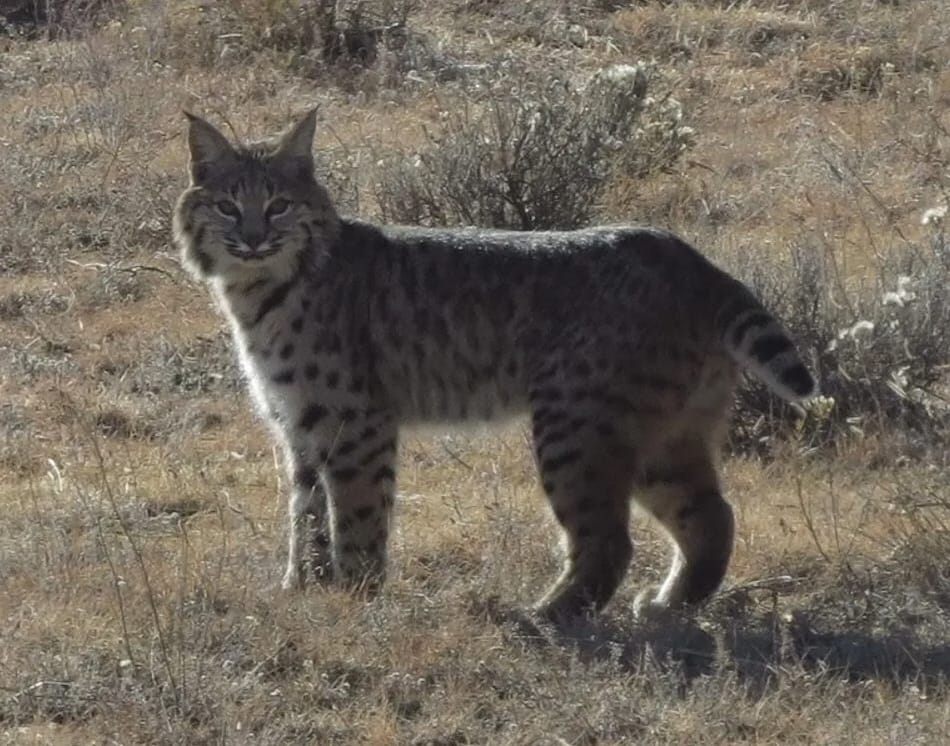
Bobcat photo by Ann Norton
This is the first in a series of articles describing wildlife native to the Golden area. The Stewards of Golden Open Space have offered to share their knowledge of the local residents.
By Ann Norton - Stewards of Golden Open Space
If you live next to, near or visit Golden’s open spaces, you may have been lucky enough to see some of our most elusive and shy neighbors, bobcats. This summer and fall they seem to be particularly evident, which led me to learn more about them. They are mammals with the scientific species name of Lynx rufus. Sometimes they are confused with and hard to distinguish from their even more elusive, secretive and larger cousins, the lynx, which are generally not found in or near Golden, but rather at higher, colder altitudes. Bobcats, the most common wild cat species, live across our state.
Typically, between 32-37 inches long with short, approximately 6-inch bobbed tails, - hence the name, bobcat - our residents have buff to brown fur, sometimes with a reddish tinge, with brown and black stripes and spots and have facial ruffs and ear tufts. The ears are black-tipped and pointed, with short black tufts, and the lips, chin and undersides are off-white in color. The tail has a black spot on the tip and white underneath and the forelegs have distinctive black stripes. As evident from the picture, they are extremely well camouflaged in their regular habitats. They have excellent hearing and vision. You will likely not see our bobcats on open prairie/grassy areas as their favored habitat include foothills, canyons, mesas and plateau with brush and woodlands. You may see them in winter as they don’t hibernate.
Bobcats have retractable claws which do not show up in tracks which are round with 4 toes and about 1.5-2.5 inches across. The claws are extended as the bobcat climbs a tree, catches prey, or defends itself.

Bobcats are carnivores, especially favoring rabbits. But not being too picky they will also eat small mammals, including rodents, as well as snakes, insects, and sometimes even birds. They typically hunt using the same routes within their territories, which for males are larger than for females.
These beautiful animals are usually silent but produce sounds during mating, like a howling house cat, and maybe deep growls, hisses, and spitting noises when they perceive a threat to their safety or territory.
Except during breeding, adult bobcats are solitary, and primarily use scent and visual signals (claw or body marks on trees or the ground) to mark their territory and communicate. According to one biological resource, “Bobcats have a sophisticated form of land tenure and usually respect each other’s territory.” However, there have been reported instances of temporary mixing of juveniles and adults, including the father in the general area of the new litter, and mixing of litters. Although they can be active during the day, most activity occurs at dawn and dusk, thus they are referred to as “Crepuscular”.
Bobcats breed in late winter and spring producing only a single litter each year typically of two to three young, after a gestation period of about 10 weeks. Neither males nor females are monogamous when it comes to mating. The female provides all the care of the young and does not tolerate the male’s presence after birth (or generally before). The nursery is a simple natural shelter – under a rock or log or in a cave that the female may line with moss and foliage. The young are nursed until they are weaned at about 8 -10 weeks of age. The kittens may travel with the mother for a few months before separating for the winter. Although females are sexually mature after one year they usually don’t mate until closer to two years of age. Males take nearly 2 years to mature. Bobcats den in places protected from the weather, which can range from hollow trees and caves to spaces under dense shrubs or between boulders.
They are stealth hunters, but they can run at speeds topping 30 miles per hour, leap at least 8 feet and are excellent climbers, including of trees, which they can seek for protection, rest, and to pursue prey. When running and hunting, they place their back feet in the same spots where their front feet have stepped to reduce noise.
According to the Colorado Department of Parks and Wildlife (CPW) “Healthy and robust bobcat populations, which Colorado’s current management is designed to maintain, are important to functioning ecosystems.” Although not currently biologically threatened the biggest threat bobcats face is the loss of their habitat, which is a growing concern everywhere including here.
In Colorado, CPW biologists assess five different metrics each year to make sure bobcat populations are healthy, which they currently are. Hopefully we are all thankful for the privilege of sharing this land with these beautiful, interesting creatures and will do what we can to ensure this continues.
Resources:
https://cpw.state.co.us/species/bobcat
https://savethehuntcolorado.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Bobcat-Lion-Lynx-Management-FAQ.pdf https://www.summitdaily.com/news/summit-outside-the-bobcat-one-tough-critter/ https://ielc.libguides.com/sdzg/factsheets/bobcat/summary https://nationalzoo.si.edu/animals/bobcat
https://bouldercountyopenspace.org/i/wildlife/bobcat/
Golden History: Golden’s Indigenous Heritage

Chief Colorow - Denver Public Library Western History Collection
Click to enlarge
by Paul Haseman
Native Americas
14 October 2024 is Indigenous Peoples Day. It is also Columbus Day. Columbus “discovered” America, but America had been discovered for more than 40,000 years by Native Americans. Today, there are more than 574 federally (BIA) recognized tribes.
Native Americans are omnipresent with the names of states, counties and cities. We honor Native Americans in many subtle ways. For example: Alabama, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Mississippi, Michigan, Texas, Arkansas, Utah, Kentucky, Oklahoma, Wyoming, Alaska, Illinois, North and South Dakota, Iowa, Tennessee, Ohio, Nebraska, Kansas, Hawaii and Missouri.
More than names, Native Americans influenced the formation of the United States. During the 1787 Constitutional Convention, John Adams published a three-volume handbook including texts from Montesquieu and John Locke. One long reference is to the Iroquois Confederation of “Six Nations,” the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, Seneca and Tuscarora. They had a Grand Council comprised of 59 chiefs (“sachems”). Our republic form of government is certainly not identical, but more resembles this confederation than any other world government at that time. Our Constitution is influenced by the Iroquois Confederation.
Movement of Tribes
History records the forced movement of 100’s of Indian tribes by Euro-Americans.
However, before the arrival of Euro-Americans, the Indian tribes themselves forced other tribes to relocate.
Likewise, many tribes voluntarily migrated to include the Cheyenne and Arapaho from Wisconsin and Minnesota beginning around 1680. The introduction of horses and their value in hunting buffalo was a major contributor to the tribes’ migration to the Great Plains.
And as the tribes migrated, they took their language with them. For example, the Algonquin language from present-day Quebec is the native language 2000 miles west of the Arapaho and Cheyenne.
So, migrations, forced and unforced, did occur before the appearance of Euro-Americas.

Forced Relocation – Euro-Americans
The Trail of Tears refers to the forced relocation to Oklahoma Territory in 1830-1850 of five civilized tribes from the Southeast; Creek (Muskogee), Choctaw, Cherokee, Chickasaw and Seminole. “Civilized” is a pertinent term. Several of the tribal towns had city halls, schools, newspapers, and homes. Many, many were not living in crude huts or tipis (teepees).
The Trail of Tears represents just one example of many unfortunate forced relocations. Treaties were signed with some compensation then those treaties were broken and new treaty after was signed with the “forced” movement of tribes. Many tribes were moved several times.
From the Euro-American perspective, treaties afforded a legal way to erode Native American land holdings and promote settlement on tribal territory.
Random Fact: The phrase “God willin’ and the creek don’t rise” was written in a letter by Benjamin Hawkins, the federal Superintendent of all tribes south of the Ohio River. When summoned to Washington, he wrote this phrase as to his potential attendance. He was referring to the Creek tribe.

Golden
The history of Golden, Colorado, from 1859 onward is well known to many Goldenites.
Excluded from Golden’s historical narrative is the history of the indigenous people who occupied the Front Range region. To address this disparity, the City of Golden published (2022) an ethnographic study, “Indigenous Connections,”
in partnership with Native Americans to document the history of indigenous people in this region. The study is available on the Golden History Museum website.
The Clear Creek Valley is situated within the ancestral territory of multiple tribes; mainly the Cheyenne (Tsistsistas), Arapaho (Hinono’ei) and Ute (Nύuchiu).
But before those tribes, archeological digs in the Golden area, such as in Apex Gulch, document Native Americans in Golden as far back as 12,000 years.
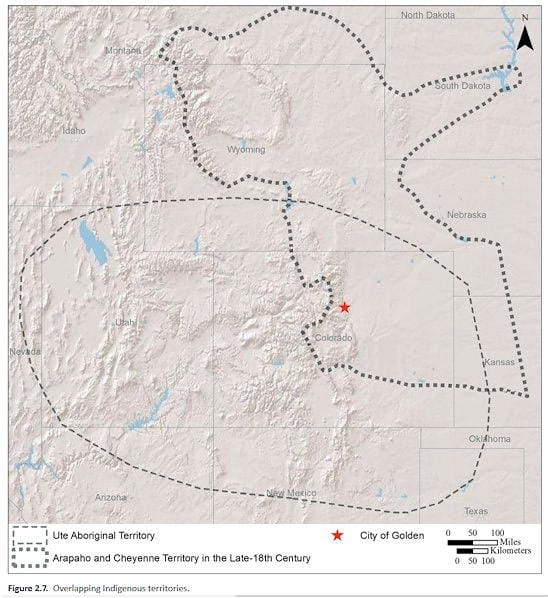
Historically, the Cheyenne and Arapaho were allies. Not so with the Utes. Conflicts between the Utes and the Cheyenne/Arapaho prior to Golden’s founding were many.
As seen in the chart, the tribal territories overlapped with Golden right in the middle. The Utes occupied the mountains but hunted on the Plains, while the Arapaho and Cheyenne were Plains Indians.
Ute Tribe
The Utes have an Aztec origin with three basic tribes, the Northern/Mountain Ute, the Southern Ute and the Ute Indian Tribe with regional “bands.” In the Golden area three bands overlapped; the Uncompahgre, Moghwachi, and Tabeguache, with the Moghwachi the most prevalent along the Front Range.
Although basically a mountain tribe, Utes hunted buffalo and seasonally came to the Plains via Ute Pass west of Colorado Springs and via Clear Creek.

Relations with early Spanish settlements were varied but became worse after an 1854 attack on the Pueblo trading post by the Utes and Apaches. The trading post was abandoned. Matters further deteriorated with the discovery of gold in the Rockies leading to the influx of Euro-Americans.
Several treaties (1850, 1863, and 1868) removed the Utes from much of Colorado, although many Utes continued to travel throughout the mountain region into the 1900’s. Today the Mountain Ute and Southern Ute have reservations in southwest Colorado.
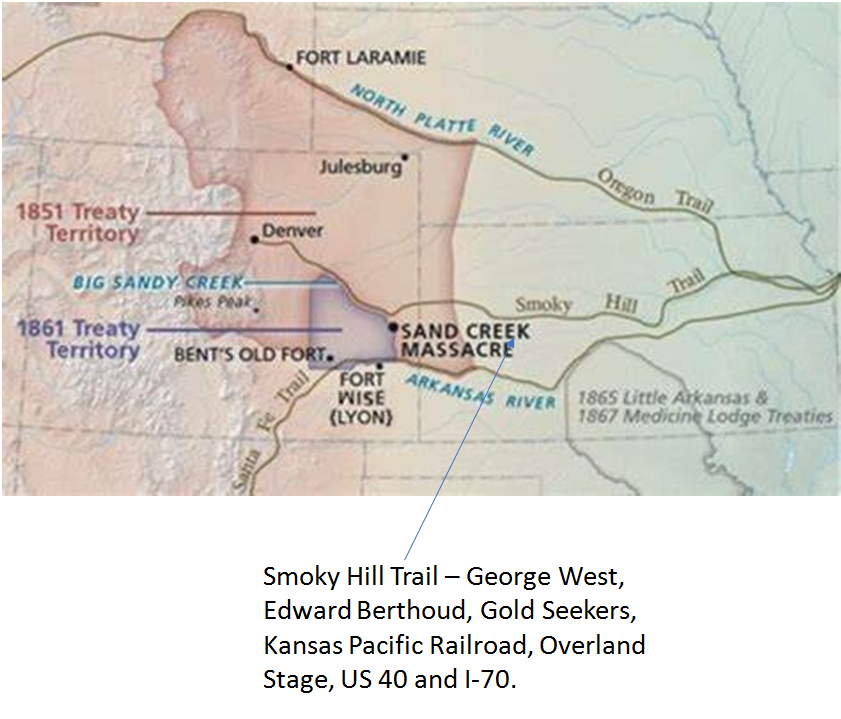
Sand Creek Massacre
The Sand Creek Massacre is a black mark on Colorado and America.
The 1851 Ft. Laramie Treaty verified ownership of a vast portion of Colorado by Cheyenne and Arapaho tribes. With the discovery of gold in 1858, easterners poured into Colorado creating conflicts and leading to the 1861 Treaty of Ft. Wise. This treaty vested a smaller area to the tribes but also established the first Cheyenne/ Arapaho Reservation, located along the north bank of the Arkansas River.
Still many Coloradans sought ways to arouse enmity toward these tribes. Minor raids by a few rogue tribal members further ignited passions. Governor John Evans sought and received authority from the War Department to take action. Evans issued a proclamation to “kill all hostile Indians.” Evans formed a 100-day volunteer militia (the 3rd Colorado Calvary) and staged the attack at Ft. Lyon. From there on 29 November 1864, the 3rd Calvary and other federalized militia under Col John Chivington opened fire on a peaceful camp of the two tribes on Sand Creek killing 230, mostly women and children. Notably, some military units refused to participate.
Although Golden was the Territorial capitol, Governor Evans celebrated this harsh action with a parade in Denver.
Congressional and BIA investigations followed, which condemned the military action. As a result, President Andrew Johnson fired Territorial Governor Evans on 1 August 1865. Years later the Southern Arapho tribe succeeded with the US Board of Geographic Names to rename Mr. Evans as Mt. Blue Sky.
The Sand Creek Massacre National Historical Site preserves the location of this brutal action
The unfortunate upshot of this massacre was to the complete removal of the Cheyenne and Arapaho tribes from Colorado to Montana, Wyoming, and Oklahoma.
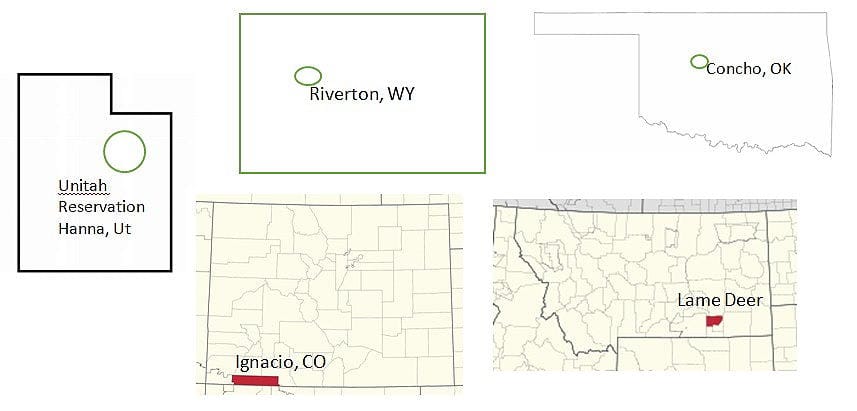
Tribal Locations Today
The Northern Arapaho are now located on the Wind River Reservation near Riverton, Wyoming. The Northern Cheyenne tribe is located in Lame Deer, Montana. The Southern Arapaho tribal headquarters, which they share with the
Southern Cheyenne Tribe, is primarily located in the communities of Concho and El Reno, Oklahoma.
The only two Indian reservations in Colorado are in the southwest corner for the Southern Ute and Ute Mountain tribes. The third, Ute Indian Tribe has its reservation at Hanna, Utah.
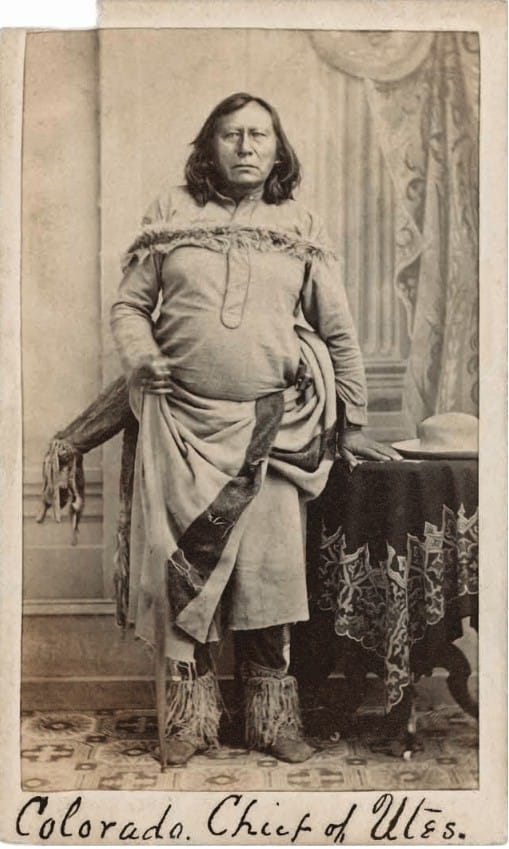

Chief Colorow
Chief Colorow was a Ute Mountain chief but originally a Comanche,
kidnapped by the Utes at age five and renamed Colorow for his “red”
skin compared to the Aztec origin Utes.
He was successful in many endeavors to include grazing and selling
horses to Goldenites and other Jefferson County residents on land,
which later became the nearby Rooney Ranch.
Although Colorow participated in the major battle with the Cheyenne
and Arapaho in ≈ 1839, by the time Golden was settled, the Utes and
Cheyenne/Arapaho in the Golden area were not at war. Chief Colorow
visited Golden often to include several Transcript interviews with publisher, George West.
Colorow earned his place in the Jefferson County Hall of Fame for his contributions to the County and “to our State and Nation.”
Colorow Point on Lookout Mtn near the Buffalo Bill Museum is named for Chief Colorow.
Summary
The Arapaho, Cheyenne and Ute tribes have long-standing connections to Golden and the Front Range with Golden located within the homelands of all three tribes.
These tribal histories, some painful, are historically linked to the development of the Golden area and are therefore essential components of the Native-American history of the area.
The City of Golden today recognizes these tribal connections, and they are an essential part of Golden History.
Many thanks to Paul Haseman for this timely exploration of Golden's native heritage.
Supporters
Many thanks to the people and organizations who support What’s Happening in Golden? If you would like to support local news, please CLICK HERE!

Sponsors:
($100/month and up)
Buffalo Rose, Buglet Solar, Foothills Art Center, Golden City Brewery, Golden Cultural Alliance, Miners Alley Performing Arts Center, The Golden Mill, Golden Chamber of Commerce, Golden History Tours, Morris & Mae Market, Miners Saloon, Colorado Railroad Museum, Golden Hayride Outpost, Kona Bowls, Unite Fitness, Tom Reiley, Michael Mason, and Esther Kettering
Friends:
($50-99.99/month or $550/yr)
Tall Pines Painting, Baby Doe’s Clothing, Goozell Yogurt & Coffee Paul Haseman, Donna Anderson, Carol & Doug Harwood, Beth Bidwell, Stephanie Painter, Greg Poulos, Joy Brandt, Ann Norton & Jonathan Storer, Mary & Don Parker, Saré Merrigan, and Nannette Johnson
Supporters:
($25-49.99/month or $250/yr)
Laura King and Scott Wilson, Bobby German and Alison McNally, Forrest Jones, Barry & Liz Bettis, Cheryl & Tom Schweich, Marjorie Sloan, Chris and Joyce Davell, Rick Flint, Forrest Jones, AC Development, Cynthia Merrill Tamny, Stephen Pero, Meg Van Ness & Steve Kalasz, Steve & Karla Schaefer, and Bud Rockhill
Members:
($10-24.99/month or $110/yr)
Brad Miller & Julie Bartos, Holly Thomas, Jim and LouAnne Dale, Ann Pattison, Thomas Hoffman, Carol Abel, Brian Quarnstrom, Sandra Curran, Bobby German and Alison McNally, Kathy Smith, Karen Smith, Carlos & Nancy Bernal, Robert Storrs, Michele Sannes, Elaine Marolla, Dixie Termin & Ron Miller, E Tom Hughes, Crystal M Culbert, Patrick A. Madison, Alice Madison & Jim Kalivas, Deb Goeldner, Christopher Ball, 6th Chair Home Services, Dot & Eric Brownson, Rosemary Coffman, Emeline Paulson, Casey & Gina Brown, Sandy Schneider, Mark and Cathy Pattridge, Cheryl G Leidich, Jen Rutter, Carol Abel, Frani R Bickart, Jennings and Litz, Bill Sedgeley, Nancy Hughes, Justin L Wade, Kathi Eggers, Traci Case, Donna Owen, Leslie D Lutz, Karen Oxman, Catherine Skokan, Ross Fraser, Lynne Haigh, Elizabeth Hilliard, Frank Young & Terre Deegan-Young, Kathy Hirons & Jack Markin, Jess & Anthony Monasterio, Ella Lyons & Jeanne Fritch, Heather Duncan, Lee Ann & Pete Horneck, Carol Cameron, Cheryl Williamson, San Daugherty, Jim Garner, John and Carol McEncroe, the Golden Welcome Center, the Golden Transcript, Koshare Eagle, and Ken and Colleen Krantz.
Followers:
($5-9.99/month)
Golden Community Garden, Lora Haimes, Mariane Erickson, J.J. Fraser





